THE BASICS
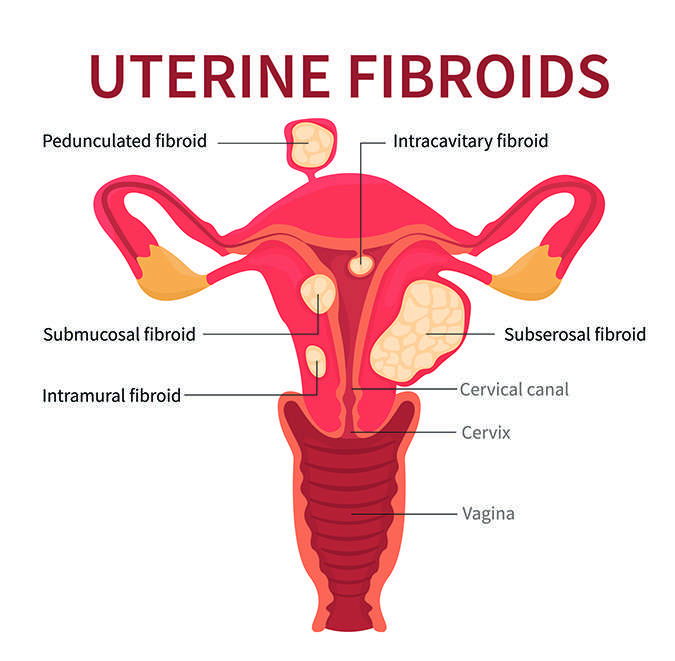
Uterine fibroids are benign (non-cancerous) tumors that form in the wall of the uterus. Fibroids can grow as a single tumor, or there can be many of them in the uterus.
Research has shown that prolonged exposure to estrogen affects fibroid growth such as during a woman’s reproductive years, and that fibroids shrink when there is low levels of estrogen, such as following menopause.
Up to 80% of women have fibroids by age 50.
Symptoms of
Uterine Fibroids
Research shows between 20%- 50% of women who have fibroids have symptoms that affect their quality of life. Fibroid symptoms can vary based on the size of the fibroid, number of fibroids present and where the fibroids are located in the uterus.
In addition to symptoms, some other problems fibroids cause:
1-3% of women with fibroids have issues with getting or staying pregnant. Depending on their size and location, fibroids can block the entrance to your uterus, interfere with the sperm’s ability to get to the egg, or change the shape of the cervix or uterus, interfering with embryo implantation.
HOW ARE UTERINE FIBROIDS DIAGNOSED?
Fibroids are most often found during a routine pelvic exam. To confirm the size and location of the uterine fibroids, your doctor may request an MRI to view the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes
90% of women have resolution of fibroid related symptoms after UFE.
A United Fibroid & Vascular board-certified physician will discuss with you whether UFE is a good treatment option for you taking into account your lifestyle, type, size, and position of the fibroids, and any risks they may present.
If you are pregnant, have already gone through menopause, or do not have any symptoms, you would typically not be a candidate for UFE treatment.






